Advanced Usage
This section describes the various features and options of ClipKIT.
Modes
This section describes the trimming modes implemented in ClipKIT. If you are unsure which is appropriate for you, we recommend using the default smart-gap trimming mode.
ClipKIT can be run with fifteen different modes, which are specified with the -m/–mode argument. Default: ‘smart-gap’
smart-gap: dynamic determination of gaps threshold
entropy: trim sites above a normalized Shannon entropy threshold (default: 0.8)
gappy: trim all sites that are above a threshold of gappyness (default: 0.9)
block-gappy: trim contiguous runs of sites above a threshold of gappyness (default: 0.9)
gappyout: infer a gap threshold from alignment-wide gap distribution and trim above it (gappyout-inspired behavior; not strict trimAl compatibility)
composition-bias: trim sites above a normalized composition-bias threshold (default: 0.8)
heterotachy: infer a parsimony guide tree and trim sites with high clade-to-clade entropy variation (default: 0.8)
kpic: keep only parsimony informative and constant sites
kpic-smart-gap: a combination of kpic- and smart-gap-based trimming
kpic-gappy: a combination of kpic- and gappy-based trimming
kpi: keep only parsimony informative sites
kpi-smart-gap: a combination of kpi- and smart-gap-based trimming
kpi-gappy: a combination of kpi- and gappy-based trimming
c3: remove third codon position from alignment
cst: custom site trimming (remove sites specified by the user)
# smart-gap-based trimming
clipkit <input>
clipkit -m smart-gap
# gappy-based trimming
clipkit <input> -m gappy
# block-gappy trimming
clipkit <input> -m block-gappy
# gappyout-style trimming
clipkit <input> -m gappyout
# entropy-based trimming
clipkit <input> -m entropy
# composition-bias trimming
clipkit <input> -m composition-bias
# heterotachy trimming (parsimony guide tree based)
clipkit <input> -m heterotachy
# kpic-based trimming
clipkit <input> -m kpic
# kpic- and smart-gap-based trimming
clipkit <input> -m kpic-smart-gap
# kpic- and gappy-based trimming
clipkit <input> -m kpic-gappy
# kpi-based trimming
clipkit <input> -m kpi
# kpi- and smart-gap-based trimming
clipkit <input> -m kpi-smart-gap
# kpi- and gappy-based trimming
clipkit <input> -m kpi-gappy
# remove third codon position
clipkit <input> -m c3
# conduct site-specific trimming
clipkit <input> -m cst -a <auxiliary file>
Output
By default, output files will have the same name as the input file with the suffix “.clipkit” appended to the name. Users can specify output file names with the -o option.
# specify output
clipkit <input> -o <output>
Log
It can be useful to have information about each position in an alignment. For example, this information could be used in alignment diagnostics, fine-tuning of trimming parameters, etc. To create the log file, use the -l/\-\-log option. Using this option will create a four-column file with the suffix ‘clipkit.log’. Default: off
col1: position in the alignment (starting at 1)
col2: reports if site was trimmed or kept (trim or keep, respectively)
col3: reports if the site is parsimony informative or not (PI or nPI, respectively)
col4: reports the gappyness of the position (number of gaps / entries in alignment)
clipkit <input> -l
Complementary
Having an alignment of the sequences that were trimmed can be useful for other analyses. To obtain an alignment of the sequences that were trimmed, use the -c/\-\-complementary option.
clipkit <input> -c
Output file with the suffix ‘.clipkit.complement’
Codon
Trims codon-based alignments. If one position in a codon should be trimmed, the whole codon will be trimmed. To conduct codon-based trimming, use the -co/\-\-codon argument.
clipkit <input> --codon
# or
clipkit <input> -co
Custom site trimming (cst mode)
Custom site trimming specified using a tab-delimited text file specified using the -a argument.
clipkit <input> -m cst -a <auxiliary_file>
The auxiliary_file is a two column tab-delimited file wherein the first column is the site (starting at 1) and the second column specifies if the site should be kept or trimmed using the strings “keep” or “trim”.
cat auxiliary_file.txt
1 keep
2 trim
3 keep
4 keep
5 keep
6 keep
Alternatively, users can specify sites that are only kept or trimmed using the auxiliary_file. For example, the following would be equivalent to the auxiliary file described above.
cat auxiliary_file.txt
2 trim
Similarly, the following would conduct the trimming, wherein the second site is removed but all others are kept.
cat auxiliary_file.txt
1 keep
3 keep
4 keep
5 keep
6 keep
Gaps
Positions with gappyness greater than threshold will be trimmed. Must be between 0 and 1. (Default: 0.9). This argument is ignored when using the kpi and kpic modes of trimming as well as an iteration of trimming that uses smart-gap or gappyout. In entropy mode, this value is treated as a normalized Shannon entropy threshold (default: 0.8).
To specify a gaps threshold, use the -g/\-\-gaps argument.
clipkit <input> --gaps 0.4
# or
clipkit <input> -g 0.4
Gap Characters
Specifies gap characters used in the input file. For example, “NnXx-?” would specify that “N”, “n”, “X”, “x”, “-”, and “?” are gap characters. Note, the first gap character cannot be “-” because the parser will interpret the gaps list as a new argument.
clipkit <input> -gc NnXx-?
Sequence Type
Specifies the type of sequences in the input file. The default is auto-detection of sequence type. Valid options include aa or nt for amino acids and nucleotides. This argument is case insensitive. This matters for what characters are considered gaps. For amino acids, -, ?, *, and X are considered gaps. For nucleotide sequences, the same characters are considered gaps as well as N.
clipkit <input> -s aa
Use this option to specify that input sequences are amino acids.
clipkit <input> -s nt
Use this option to specify that input sequences are nucleotides.
Ends only
For a given trimming mode, this option trims only sites at the ends of an alignment. For example, if the sites that should be trimmed include [0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 14, 15, 16] for smart-gap mode and an alignment of length 16, adding the ends_only mode will result in [0, 1, 2, 14, 15, 16] being the sites that will be trimmed. Use this argument with -eo, --ends_only.
clipkit <input> -eo
# or
clipkit <input> --ends_only
Threads
ClipKIT supports parallel processing for site classification and character frequency calculations. For larger alignments, this can significantly speed up processing.
The number of threads can be specified using the -t/\-\-threads argument. Default: 1
# Single-threaded processing (default)
clipkit <input>
# Multi-threaded processing with 4 threads
clipkit <input> -t 4
# or
clipkit <input> --threads 4
Performance Notes:
Parallel processing is activated adaptively based on alignment size and requested threads
For smaller alignments, single-threaded mode is typically faster due to multiprocessing overhead
The optimal number of threads depends on your system and alignment size
For KPI/KPIC family modes (kpi, kpi-gappy, kpi-smart-gap, kpic, kpic-gappy, kpic-smart-gap), ClipKIT may automatically use fewer threads than requested when that is expected to be faster
Results are identical regardless of the number of threads used (fully reproducible)
Dry run
Use dry run mode to execute trimming and compute summary statistics without writing alignment, complementary, or log output files.
clipkit <input> --dry_run
Validate only
Use validate-only mode to check input format and argument consistency (including
auxiliary file checks for cst mode) and then exit without trimming.
clipkit <input> --validate_only
Report JSON
Write a machine-readable JSON report with run configuration and outcome details.
# explicit report path
clipkit <input> --report_json run_report.json
# default report path: <output>.report.json
clipkit <input> --report_json
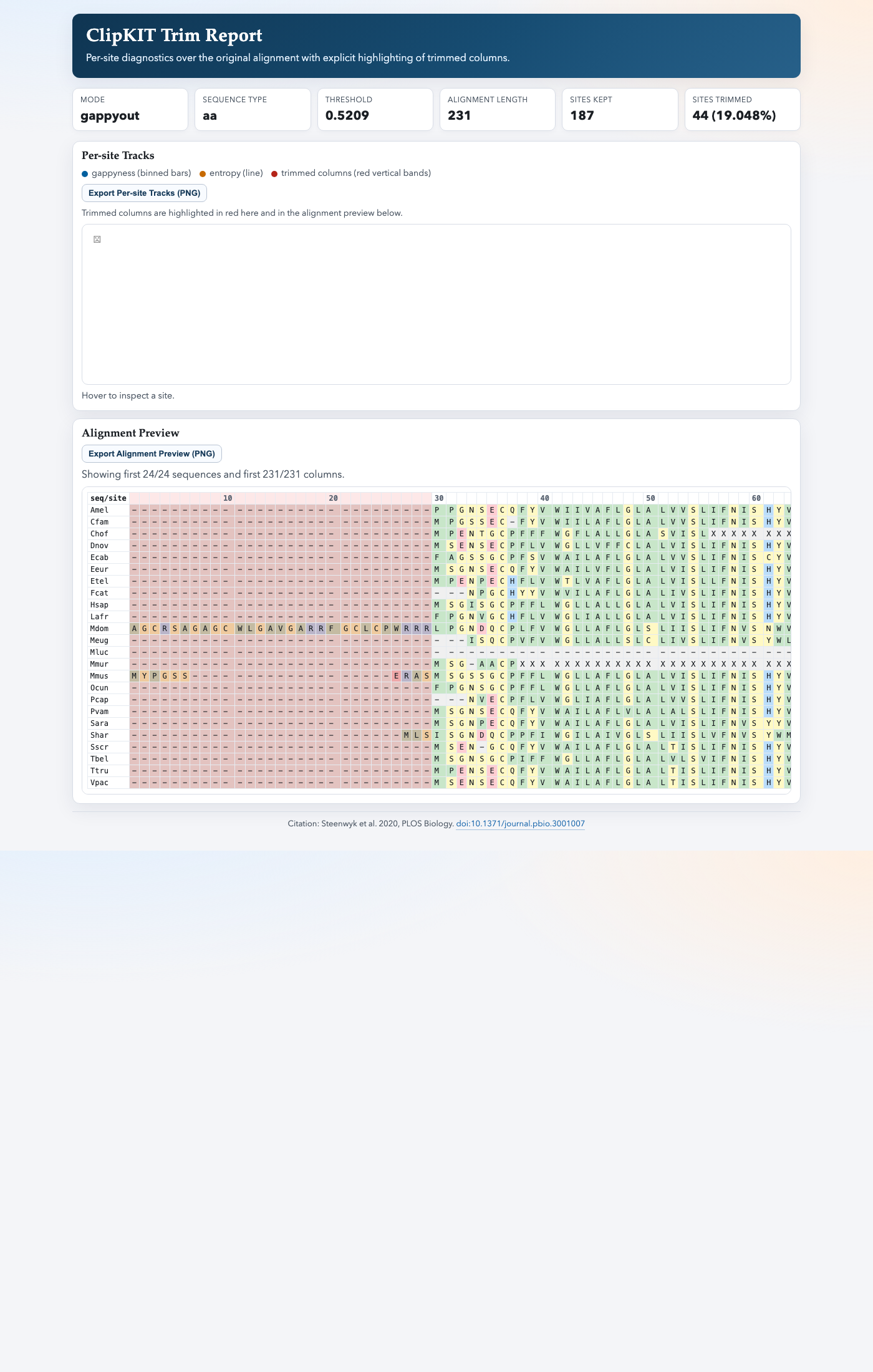
Plot trim report
Write an interactive HTML report with per-site tracks and trimmed-column highlighting.
# explicit report path
clipkit <input> --plot_trim_report run_plot.html
# default report path: <output>.trim_report.html
clipkit <input> --plot_trim_report
The report includes:
Per-site gappyness bars and entropy line plot
Highlighting of trimmed columns in both tracks and alignment preview
Amino-acid or nucleotide coloring in the alignment preview (auto-detected)
Export buttons for saving per-site tracks and alignment preview as PNG files
Example preview:
All options
Option |
Usage and meaning |
|---|---|
|
Print help message. |
|
Print software version. |
|
Specify trimming mode (including |
|
Specify output file name. |
|
Specify threshold (between 0 and 1): gappyness for most modes, normalized entropy for |
|
Specify gap characters used in input file (AAs: |
|
Conduct codon-based trimming. Default: off. |
|
Specify sequence type of input file ( |
|
Specify input file format*. Default: auto-detect. |
|
Specify output file format*. Default: input file type. |
|
Create a log file. Default: off. |
|
Create a complementary alignment file. Default: off. |
|
Auxiliary file used for specifying sites to trim in |
|
Trim only sites at alignment ends that would otherwise be removed. Default: off. |
|
Disable logging to stdout. Default: off. |
|
Requested threads for parallel processing; KPI/KPIC modes may auto-tune lower. Default: 1. |
|
Run trimming/stat calculations but skip writing output files. Default: off. |
|
Validate inputs/arguments and exit without trimming. Default: off. |
|
Write a JSON run report; if no path is given, uses |
*Acceptable file formats include: fasta, clustal, maf, mauve, phylip, phylip-sequential, phylip-relaxed, stockholm